本文主要讲 service worker 的主要基本特性以及使用方法,从实际开发的 PWA 中学习 service worker。
Service Worker 是什么
Service Worker 是一个运行在在浏览器后台,独立于网页运行的由事件驱动的脚本。
本质上是 Web Worker 的一种具体实现,通常与 Cache API 相结合使用,因为 Worker 线程执行的脚本与网页脚本相独立的缘故,
Worker 线程内不能访问到 window 以及 dom 相关的数据。同时,在 Service Worker 中处理大量数据时也不会阻塞的主线程。所以通常可以在 Service Worker 线程中拦截浏览器的请求,读取和存储请求内容,进而实现离线应用。
Service Worker 能做什么
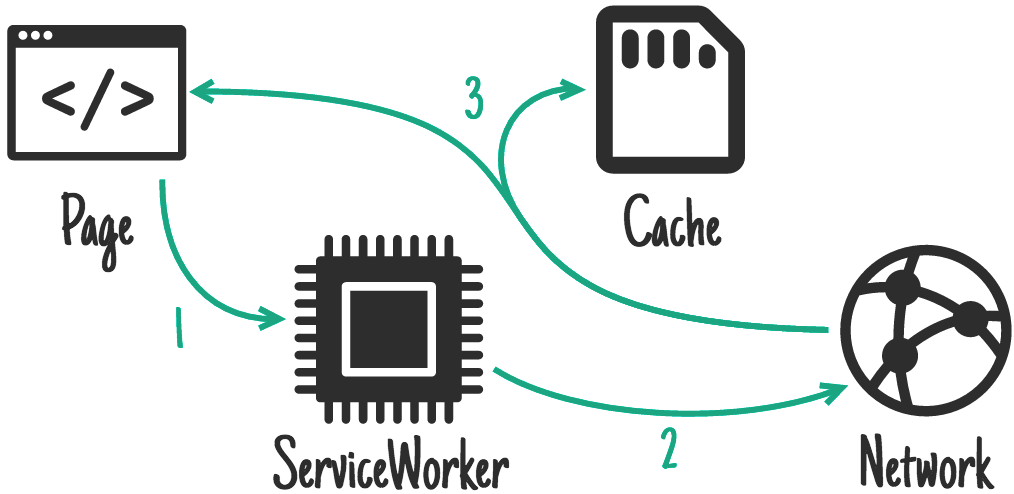
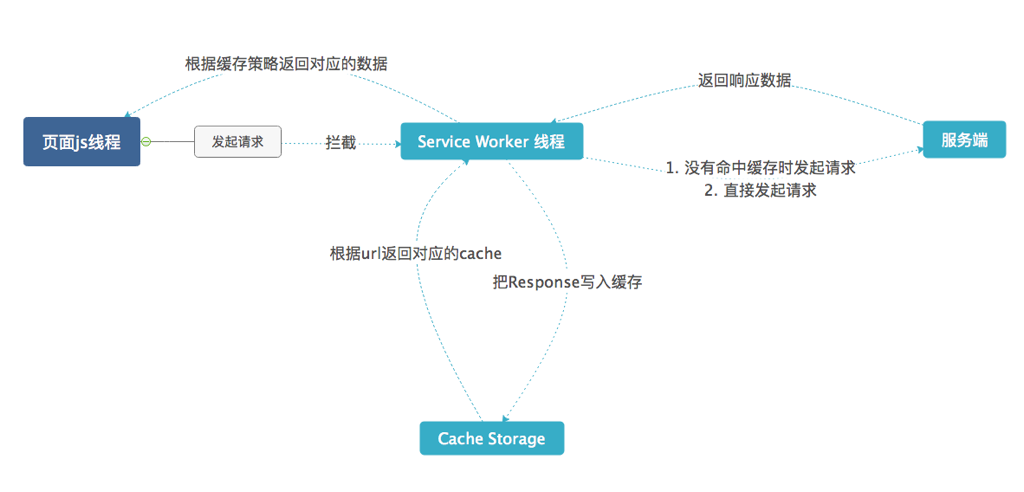
当客户端发起请求时,Service worker会先请求对应的资源,并把结果返回,同时在cache storage中存储一份。在出现网络不可访问或服务出错时可以从缓存中获取相同的资源做容灾处理。
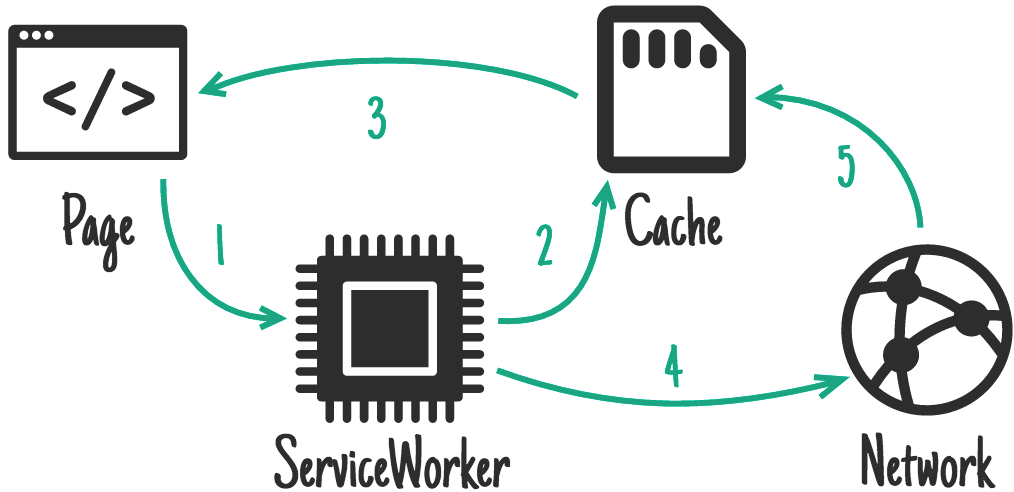
当客户端发起请求时,Service worker会先从cache storage中读取资源,并把结果返回,同时请求一份资源,成功的话更新到缓存中。这样可以保持极快的响应速度,适用于更新频率不高的资源。
Service Worker 的基本架构
- 独立的声明周期
- 基于
Web Worker的事件机制
Service Worker 的生命周期
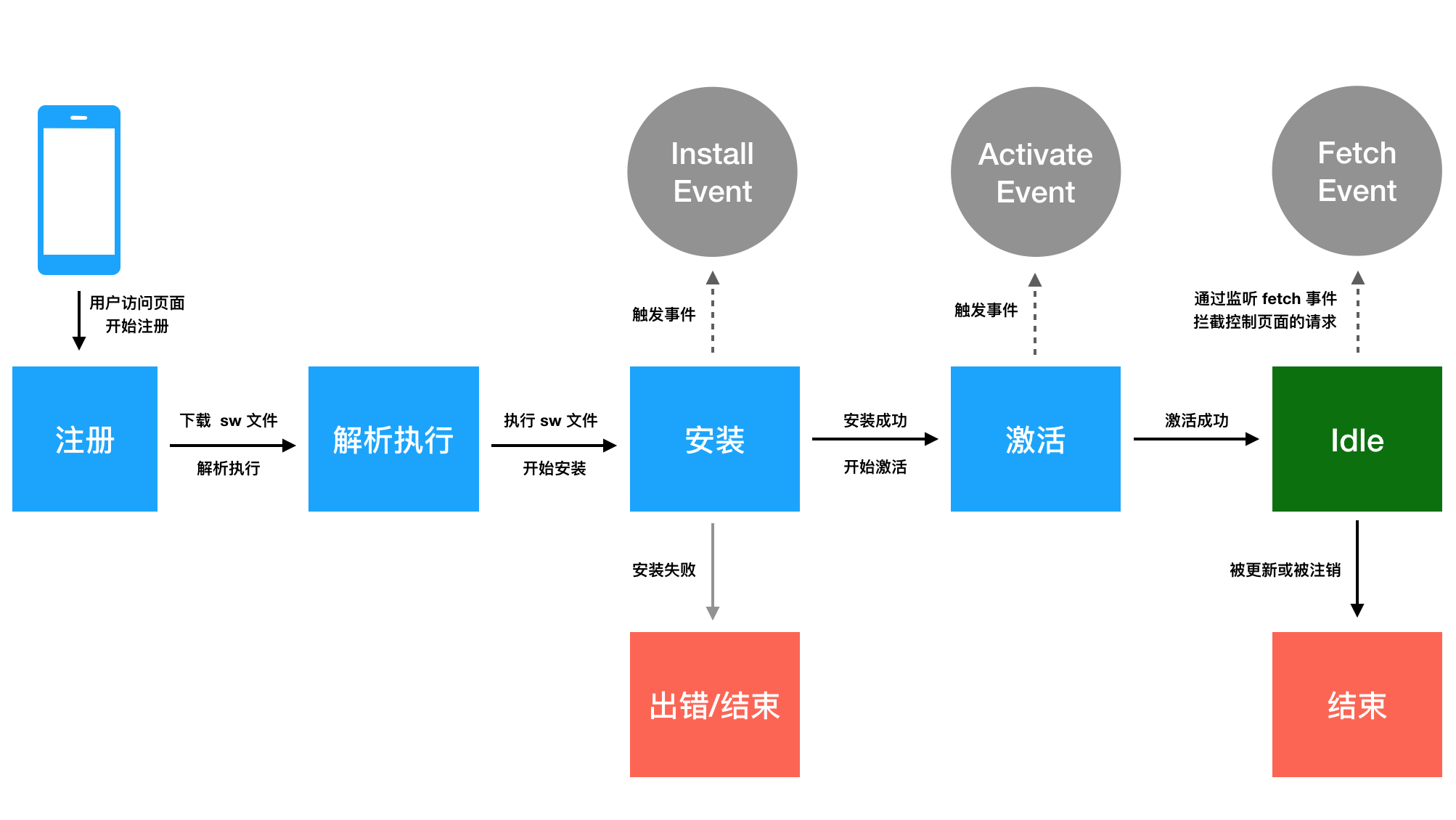
Service Worker 生命周期的目的:
- 实现离线优先。
- 允许新 Service Worker 自行做好运行准备,无需中断当前的 Service Worker。
- 确保整个过程中作用域页面由同一个 Service Worker(或者没有 Service Worker)控制。
- 确保每次只运行网站的一个版本。
Service Worker 有独立的一套生命周期,生命周期主要分为
注册
注册是指浏览器下载
Service Worker文件并确认其作用域的过程。
简单的理解就是浏览器去下载你指定的js,然后解析运行
那么作用域是什么呢?
作用域是指Service Worker能够访问的的资源范围。
举个栗子
- 域名A:https://mei.youzan.com/a/b
注册 SW 时 sw 文件在A域名下,则 SW 的作用域为 /a/b,那么这个 SW 只能处理 /a/b/xxx.png 这一类资源 - 域名B:https://mei.youzan.com
注册 SW 时 sw文件在B域名下,则 SW 的作用域为 /,那么这个 SW 能处理 根路径 下的所有静态资源
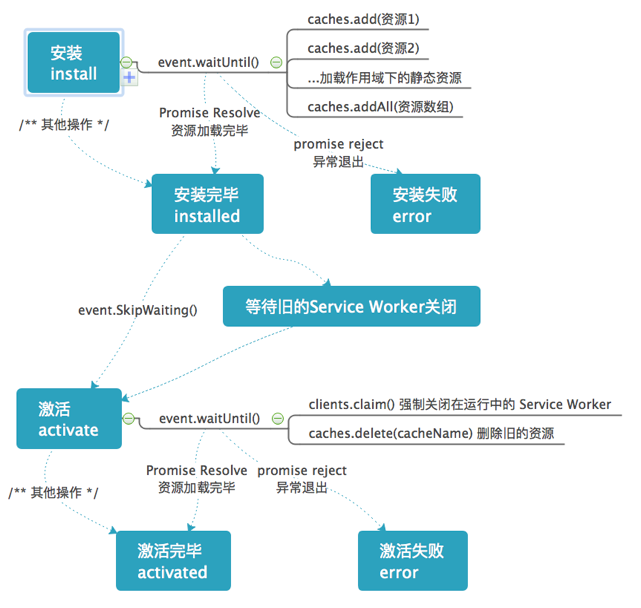
安装
JS 文件下载解析完后运行,然后开始安装过程,这个过程会触发一个 install 事件。
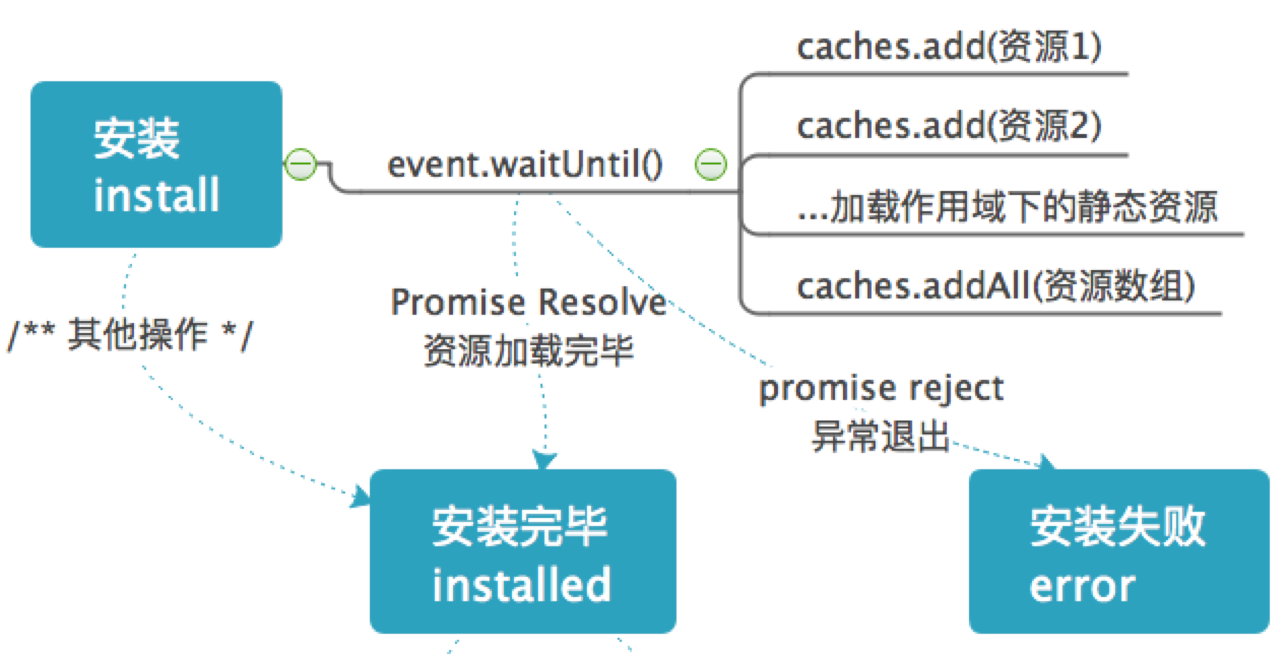
通常安装阶段会分为三部分:
- install 安装阶段刚开始,使用 event.waitUntil() 可以使状态流转进 installing,否则直接进入 installed
- installing 安装中,这是时候一般会进行静态资源的缓存。缓存过程中状态会在 installing 中等待直到缓存结束
- installed 安装完毕,从 installing 状态流转而来
举些栗子
监听install事件
1 | /** servie-worker.js */ |
监听install事件,并缓存静态资源
1 | /** servie-worker.js */ |
激活
安装完成后,
Service Worker还未开始真正运行,激活过程就是Service Worker启动的过程
通常安装阶段会分为三部分:
- activate 安装阶段结束后流转的状态,使用 event.waitUntil() 可以使状态流转进 activating,否则直接进入 activated
- activating 激活中,这是时候一般会进行客户端页面控制权的交换,以及静态资源的迭代
- activated 激活完毕,从 activating 状态流转而来
举些栗子
监听active事件
1 | /** servie-worker.js */ |
监听active事件,删除旧的资源
1 | /** servie-worker.js */ |
这里涉及到一个更新的流程更新
以下情况下会触发更新:
- 导航到一个
Service Worker作用域内的页面。 - 更新 push 和 sync 等功能事件,除非在前 24 小时内已进行更新检查。
- 调用 .register(),仅在 Service Worker 网址已发生变化时。
活跃状态
激活后,
Service worker启动成功并进入活跃状态IDLE,这个时候可以通过它独立的事件机制去为所欲为。
Service Worker 的事件机制
Service Worker基于Web Worker,可以通过message事件实现基本的Worker和主线程间通信。
- fetch 加载资源
- sync 同步
- push 服务端消息推送
- message worker和主线程的消息监听
fetch事件
浏览器发起任何请求都会被
fetch事件监听到。
举些栗子
仅限网络请求
1 | /** servie-worker.js */ |
仅限缓存
1 | /** servie-worker.js */ |
缓存优先,网络备用
1 | /** servie-worker.js */ |
网络优先,缓存备用
1 | /** servie-worker.js */ |
缓存优先,网络备用,更新缓存
1 | /** servie-worker.js */ |
网络异常或错误处理
1 | /** servie-worker.js */ |
sync事件
TODO
push事件
TODO
有没有一劳永逸的工具
Workbox是GoogleChrome团队推出的一套 Web App 静态资源本地存储的解决方案,该解决方案包含一些 Js 库和构建工具,在 Chrome Submit 2017 上首次隆重面世。而在Workbox背后则是Service Worker和Cache API等技术和标准在驱动。在Workebox之前,GoogleChrome团队较早时间推出过sw-precache和sw-toolbox库,但是在GoogleChrome工程师们看来,Workbox才是真正能方便统一的处理离线能力的更完美的方案,所以停止了对sw-precache和sw-toolbox的维护。
从上前面介绍的 Service Worker 特性上看,我们主要是想利用它的 Cache API 操作缓存数据,比如 Precaching(预缓存)、Runtime caching(运行时缓存),但是又不想写太多模板式的代码。
Workbox 则是提供了恰到好处的支持,并且提供多种 Strategies(缓存策略)优化缓存。